In this article, we’re going to talk about the switch and router, and the difference between router and switch.
With the increasing number of desktop computers, notebooks and laptops at home, routers and switches are gradually becoming more widely known by people in order to enable these electronic devices to access the internet together. Since home routers and switches look very similar from the outside, many people don’t know the difference between routers and switches, and what they can do. So we’re going to look at the difference between router and switch in this article.
What Is A Switch?
A switch is a network device used for electrical (optical) signal forwarding, which can provide an exclusive electrical signal path for any two network nodes connected to the switch. The switch recognizes and completes the forwarding of Ethernet data frames based on the MAC (Media Access Control) address. Usually, the switches include Ethernet switches, telephone voice switches, fiber optic switches and so on.

How network switch works
Data sent from a computer is forwarded through devices such as hubs, switches, and routers to its final destination. The forwarding device will find the destination IP address based on the header information in the data packet. Then the forwarding device queries its internal forwarding rule table for the export path that the data needs to be forwarded.
Routers and switches play the role of couriers. No matter whether the data packets contain application data or TPC protocol control information, they will not affect the transmission operation of the packets. That is, when you access a website in a browser, no matter what information you send, it will be identified as a data packet in the switch, and all the packets are independent in the process of transmission to the destination and have no relationship with each other.
After the data packet passes through the hub, it will be broadcast to the entire network. A hub is equivalent to a splitter, which separates an entry into multiple exits. It does not determine which exit the data packet should flow out from based on its destination address. Instead the hub directly broadcasts data packet. That’s the downside of hubs, as this way can easily cause broadcast storms.
What is broadcast storm?
The broadcast storm is when broadcast data floods the entire network, causing devices to be unable to process it and occupying a large amount of network bandwidth. It will result in the inability of normal services to operate, or even complete paralysis. Since the hub only broadcasts the signal intactly, even if the signal is distorted by noise, it will be sent to the destination as it is. This way requires devices such as switches or routers to check and find errors, and then retransmit the lost packets. But it will lead to disadvantages such as low network transmission efficiency and large network delay.
Why are switches more efficient than hubs?
The design of the network switch is to forward the network packet to the destination intactly. When the signal reaches the network cable interface, it is received by the PHY (MAU) module. When the signal comes in from the twisted pair, it enters the receive part of the PHY (MAU) module. Next, the PHY (MAU) module converts the signal in the network cable into a common format. Then it passes the signal to the MAC module. The MAC module converts the signal into digital information, and then checks the error through the FCS at the end of the packet, and stores it in the buffer if there is no problem.
A port is composed of a network cable interface and the following circuit parts. That is to say, a port on a switch is equivalent to a network card on a computer. But switches work a little differently than network cards. The network card has a MAC address. It checks the MAC address of the recipient of the packets it receives to see if they are addressed to it, and discards them if they are not addressed to it. While the port of the switch does not check the MAC address of the recipient, but directly receives all the packets and puts them into a buffer. So the switch port does not have a MAC address.
After the switch deposits the data packet in the buffer, it needs to check whether the receiver’s MAC address is already in the MAC address table. The MAC address table contains two pieces of information. One is the MAC address of the device, and the other is which port the device is connected to on the switch.
If the receiver’s MAC address is not in the MAC address table, the switch will send a broadcast packet to query the MAC address, and the packet will be broadcast to each port. After the computer connected to the switch port receives the data packet, it drops the data packet if it confirms that the data is not its own. If it is then computer will respond with a packet to the switch. From which port the switch receives the response, it writes the port and the MAC address of the response into the MAC address table, thus recording a piece of data.
However, the switch has limited storage space. The MAC address will not be added to the address table indefinitely. When the device moves, or the port changes, the MAC address table also needs to be changed. The switch will automatically delete the MAC address records that have not been used for a period of time. In this way, the switch can automatically add and delete records for a long time. And it works properly without any special measures.
What Is A Router?
A router, also known as a gateway, professionally it is a device used to connect multiple logically separated networks. The logical network represents a single network or a subnet. When data is transferred from one subnet to another, it is done through the router’s routing capabilities.
Therefore, the router has the function of judging the network address and selecting the IP path. It can establish flexible connections in a multi-network interconnection environment. Also it can connect various subnets with completely different data packet and media access methods. The router only accepts information from the source station or other routers. So it is an interconnection device belonging to the network layer.
How network router works
We all know that computers can support wireless LAN by replacing the wireless network card, and so can routers, if the port module of the router is equipped with hardware that supports wireless LAN. In addition, the router not only supports wireless communication modules, but also broadband private lines such as ADSL and FTTH. As long as the port module is installed with hardware that supports these technologies.
After receiving the data packet, to determine the forwarding destination, the router will query in the routing table according to the IP address recorded in the IP header of the received packet. Then the forwarding module transfers the packet to the port corresponding to the forwarding target. Then the port sends the packet out according to the rules of the hardware. This means that the port module sends and receives network packets as the actual sender or receiver.
Taking an Ethernet port as an example, the port of a router is different from that of a switch. It has a MAC address, so it is able to be both a sender and a receiver of Ethernet. The port also has an IP address, in the sense that it is the same as a computer’s network card. When forwarding a packet, the router port will first receive the Ethernet packet sent to itself, and then query the forwarding destination, and then the corresponding port will act as the sender to send the Ethernet packet. Each port of the router has a MAC address and an IP address. So each can send and receive data packets as a normal computer.
The general idea of “lookup table to determine the forwarding destination” is similar for routers and switches. But the process is different. The switch uses the MAC address of the receiver in the MAC header to determine the forwarding destination. Whereas the router uses the IP address. Due to the different addresses used, the content of the table that records the forwarding destination will also be different. The switch forwards the data according to the MAC address table, while the router forwards the data according to the routing table.
The record of the routing table also has something called the subnet mask, which is only used to tell the router how many bits to match when matching a destination address. Through the above method, we can also write the address of a specific computer into the routing table with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.255. It means that all 32 bits in the address are 1. In this way, if all the bits of the host number are 0, it can represent a subnet, and if the bits of the host number are not all 0, it can represent a certain computer. Both cases can be handled by the same rules.
Another item in the routing table is the hop count (also the hop count). It indicates how many routers locate before the destination IP address. The smaller the number, the closer to the destination. The larger the number, the further away from the destination.
Another entry in the routing table is the hop count, which indicates how many routers are from the destination IP address. The smaller the number, the closer to the destination. The larger the number, the further away from the destination.
The Difference Between Router and Switch
Routers are created after switches, just like switches are created after hubs. So routers and switches are also connected to a certain extent, they are not two completely independent devices. The router mainly overcomes the deficiency that the switch cannot route and forward the data packets. Connecting the networks to each other requires the use of some intermediate devices, or relay systems. According to the level of the relay system, there are the following five relay systems.
- The physical layer (that is, layer 1) is a relay system, a repeater.
- The data link layer (ie the second layer, layer 2), ie the bridge.
- The network layer (the third layer, layer 3) is a relay system, a router.
- A mixture of bridge and router, the brouter combines the functions of a bridge and a router.
- The relay system above the network layer, the gateway.
When the relay system is a repeater, it is generally not called a network interconnection. Because it is just an expansion of a network, which is still a network. Therefore, the network interconnection generally refers to the network interconnected by switches and routers. The main differences between routers and switches are reflected in the following aspects.
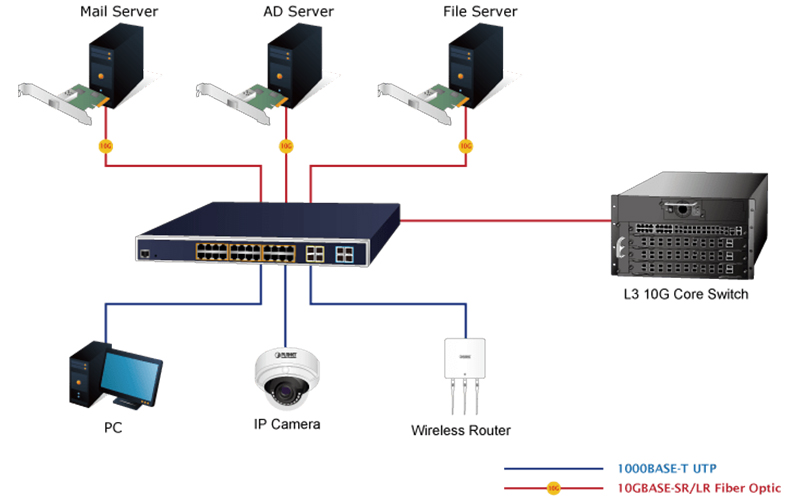
1. They work at different layers
The original switch worked at the data link layer of the OSI/RM open architecture, which is the layer 2. The router is designed to work at the network layer of the OSI model from the very beginning. Since the switch works at the layer 2(data link layer) of OSI, it works in a simpler way. While the router works at the layer 3(network layer) of OSI, where more protocol information is available. So the router can make more intelligent forwarding decisions.
2. The data forwarding is based on different objects
The switch uses the physical address or MAC address to determine the destination address for forwarding data. The router uses the ID numbers (ie IP addresses) of different networks to determine the address for data forwarding. IP addresses are implemented in software and describe the network where the device is located. Sometimes these Layer 3 addresses are also called protocol addresses or network addresses. The MAC address is usually provided by the hardware, assigned by the network card manufacturer, and has been solidified into the network card. Generally speaking, it cannot be changed. The IP address is usually assigned automatically by the network administrator or the system.
3. Traditional switches can only partition conflict domains, not broadcast domains. Whereas routers can partition broadcast domains
The network segments connected by the switch still belong to the same broadcast domain, and the broadcast packets will be propagated on all network segments connected by the switch, which can lead to communication congestion and security holes in some cases. The network segments connected to the router are assigned different broadcast domains, and broadcast data does not pass through the router. Although switches above Layer 3 have VLAN capability and can also split broadcast domains, communication between sub-broadcast domains cannot be performed, and routers are still required for communication between them.
4. The router provides the service of the firewall
The router only forwards data packets with specific addresses, and does not transmit data packets that do not support routing protocols and unknown destination network data packets, thereby preventing broadcast storms. Switches are generally used for LAN-WAN connections. Switches belong to bridges and they are the devices at the data link layer. Some switches can also implement Layer 3 switching.
Routers are for WAN-WAN connections and can resolve the forwarding of packets between heterogeneous networks, acting at the network layer. They simply accept incoming packets from one line and forward them to the other. These two lines may belong to different networks and use different protocols. In comparison, routers are more powerful than switches, but they are also relatively slow and expensive. Layer 3 switches have both the wire-speed packet forwarding capability of switches and the good control functions of routers, so they are widely used.
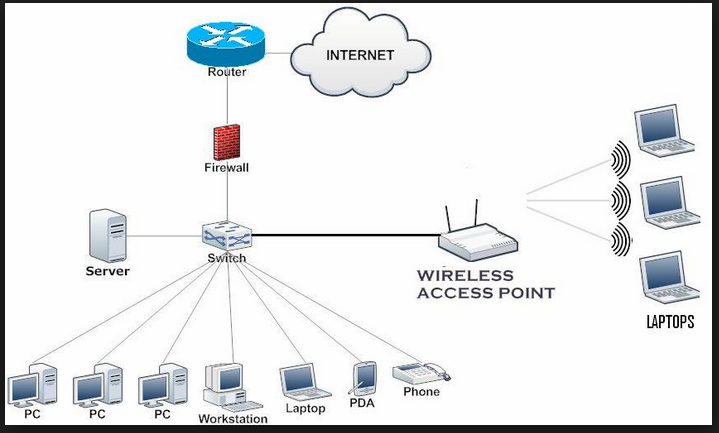
Conclusion – The Difference Between Router and Switch
The above are some differences between switches and routers. In fact, although these two devices are different in functions, they often complement each other in application scenarios. The router is for home use. It is enough when there are few computers or mobile Internet devices in your home. There is absolutely no need to buy a switch. The switch is especially used when many devices need to access the Internet. For example, dozens of computers in a company need to access the Internet. With a switch you also need the routing device to access the external network.
Switches form a local area network, and routers form a wide area network. The router is used to connect to the external network, and the switch is used to connect to the internal network. That is to say, when the company has a lot of computers, it is necessary to use a switch to expand the local area network, only router is not enough at all. If it is for home, the router is enough for you to use to access network.
